The major levels of organization in the body, from the simplest to the most complex are: atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, human organism.
The atom is the basic building block for all matter in the universe.
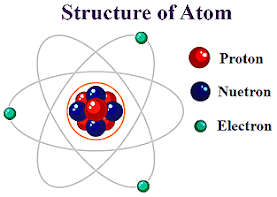
All matter is made up of substances called Elements it's a substance that consists of only one type of atom for Example: oxygen All elements are made up of atoms. Atom is the smallest unit of element are made up of proton, neutron, and electron. |
Science worksheets
CHAPTER 1: Life Science
FIRST TERM: Chemical Building Blocks of Life
LESSON 1: What is a Quark in an atom?
LESSON 2: Structures and Functions of Life Cells, Tissues, and Organs
Levels of Organization
Specialized Cells
Cell Functions and Components
Cell Components
LESSON 1: What is a Quark in an atom?
LESSON 2: Structures and Functions of Life Cells, Tissues, and Organs
Levels of Organization
Specialized Cells
Cell Functions and Components
Cell Components
LESSON 3: Cell Division: Mitosis
LESSON 4: The differences between plant cell structure and animal cell structure
Organs and Systems of the Human Organism
LESSON 5: Five Vital Organs in the Human Body
LESSON 4: The differences between plant cell structure and animal cell structure
Organs and Systems of the Human Organism
LESSON 5: Five Vital Organs in the Human Body
LESSON 6: Circulatory System: The Heart
LESSON 7: Respiratory System
LESSON 8: Muscular System
LESSON 9: Skeletal System
LESSON 13: Digestive System
LESSON 14: Nervous System
LESSON 15: Endocrine System
LESSON 16: Reproductive System
LESSON 17: Urinary System
LESSON 18: Composition of the human body
LESSON 19: Homeostasis
Nutrition Concepts
LESSON 20:DNA and Chromosomes
Alleles and Traits
Alleles and Traits
Heredity
LESSON 21: Evolution
Evolutionary Relationships
Evolutionary Relationships
LESSON 22: Ecosystems
Energy in Ecosystems
Matter in Ecosystems
LESSON 23: Food Chains
Food Webs
LESSON 23: Food Chains
Food Webs
Relationships in Ecosystems (Predator-Prey, Symbiosis)
Disruption of Ecosystems and Extinction
Disruption of Ecosystems and Extinction
CHAPTER 2: Physical Science
SECOND TERM: Matter, Elements, Chemical Interactions
LESSON 24: Structures of Matter
Atomic Particles
Ions and Isotopes
Molecules, Elements, and Compounds
Physical and Chemical Properties
LESSON 25: States of Matter
Chemical Formulas and Equations
Conservation of Mass
Balancing Chemical Equations
Types of Chemical Reactions
Solutions and Solubility
Atomic Particles
Ions and Isotopes
Molecules, Elements, and Compounds
Physical and Chemical Properties
LESSON 25: States of Matter
Chemical Formulas and Equations
Conservation of Mass
Balancing Chemical Equations
Types of Chemical Reactions
Solutions and Solubility
Saturation, Weak and Strong Solutions
LESSON 26: Types of Energy
Energy Transformations
Waves
Types of Electromagnetic Radiation
Uses and Dangers of Electromagnetic Radiation
Heat
Energy in Reactions
Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic Reactions
Sources of Energy
LESSON 27: Motion and Force
Motion
Momentum and Collisions
Force
Energy Transformations
Waves
Types of Electromagnetic Radiation
Uses and Dangers of Electromagnetic Radiation
Heat
Energy in Reactions
Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic Reactions
Sources of Energy
LESSON 27: Motion and Force
Motion
Momentum and Collisions
Force
LESSON 28: Gravity
Newton’s Laws
Mass and Weight
Newton’s Laws
Mass and Weight
LESSON 29:Work and Machines
Simple Machines
Mechanical Advantage and Power
Simple Machines
Mechanical Advantage and Power
CHAPTER 3: Earth and Space Science
THIRD TERM: Space Systems
LESSON 30: The Solar System
The Sun, moons, Asteroids and Comets
Eight Planets and Dwarf Planet Pluto
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
LESSON 31: The Universe
Stars
Earth Systems
LESSON 32:The Structure of Earth
Tectonic Plates
Tectonic Plates
LESSON 33: Earth’s Atmosphere
LESSON 34: Weathering and ErosionWind
LESSON 35: Earth's Bodies of Water
The Five Oceans
Seas
Lakes
Rivers
Other bodies of water
LESSON 36: Water Cycle
Lakes
Rivers
Other bodies of water
LESSON 36: Water Cycle
LESSON 37: Living Things and Non-living Things
LESSON 38: Life Cycle
LESSON 39: Land Biomes
LESSON 38: Life Cycle
LESSON 39: Land Biomes
tropical rainforests
savannas
deserts
chaparral (shrubland)
temperate grasslands
temperate forests
taiga (boreal forests)
tundra
LESSON 40: Water Biomes
Freshwater Biomes (Lakes, Ponds, Rivers, Streams, Wetlands)
Marine biomes
Oceans, Coral Reefs, Estuaries, Intertidal Zones,
Deep Sea, Photic Zone, Aphotic Zone